What is IVF MORE?
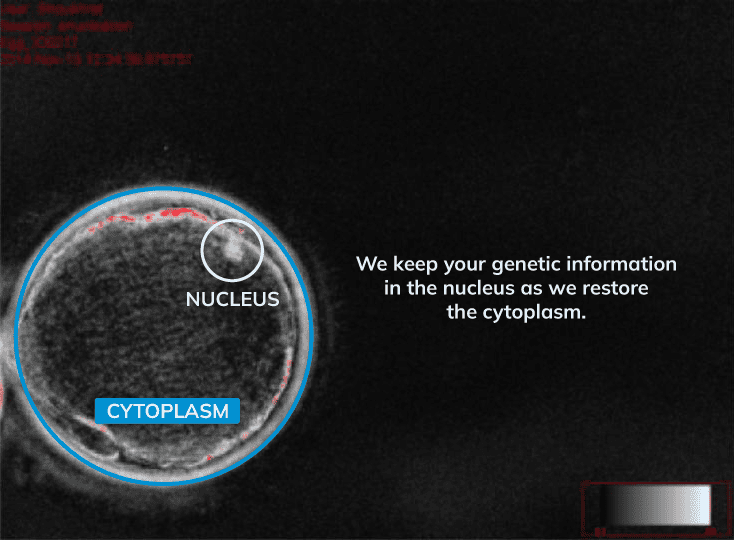
Cytoplasm restoration to improve egg metabolism while preserving your genetic material.
Traditionally, when a woman’s eggs presented metabolic dysfunction, structural disorganization, or impaired cell division, the only viable alternative was egg donation. IVF MORE® transforms this paradigm by offering a scientific, patented approach to restore and optimize a patient’s own eggs, making pregnancy possible with her own genetic material.
This procedure integrates multiple scientific advancements, including:
- Advanced metabolic egg diagnosis: Evaluation of the energy status of each egg through molecular analysis.
- Infusion of Specific Growth Factors: Use of essential metabolites to enhance mitochondrial functionality. Metabolic factors from a donor egg’s cytoplasm are injected to support cell division, while the patient’s genetic material is preserved.
- Laser especially designed for egg micromanipulation.
- Embryo Culture and Use of Magnetic Fields: After restoration and fertilization, the oocyte cytoskeleton is optimized, and embryo cell division is improved.
- The IVF MORE® technique requires that egg retrieval be performed at the specialized Ingenes laboratory in Mexico City. IVF MORE® is a technique currently in development, under patent, and with scientific articles in preparation to be published.
Live Births Per intended Egg Retrieval SART : https://sartcorsonline.com/CSR/PublicSnapshotReport?/ClinicPKID=0&reportingYear=2022
Autologous Germline Mitochondria Energy Transfer : https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5545901/pdf/nihms880936.pdf
Shoukhrat Mitalipov, Ph.D. / Center for Embryonic Cell and Gene Therapy : Meet Shoukhrat Mitalipov, Ph.D./ His pioneering work with mitochondria could help eliminate genetic disease: https://www.ohsu.edu/embryonic-cell-gene-therapy-center/meet-shoukhrat-mitalipov-phd
Magnetic Fields – Nature: https://www.nature.com/articles/srep37407
Age in Fertility
The Problem: Egg Quality Deterioration
As women age, eggs undergo metabolic and structural alterations that impact their ability to develop into viable embryos. These alterations include:
- Decreased ATP production: Poor egg metabolism affects cell division.
- Increased oxidative stress: Reactive oxygen species (ROS) damage egg DNA and mitochondria.
- Cytoskeletal disorganization: Internal structures that maintain the egg’s shape and division ability become impaired.
- Genetic signaling errors: Disruptions in gene activation required for embryo development.
These factors contribute to poor oocyte quality, failed IVF cycles, cycle cancellations, embryo arrest, and the formation of abnormal embryos (with chromosomal alterations), increasing the risk of pregnancy loss and implantation failure.
The Solution: Egg Restoration with IVF MORE®
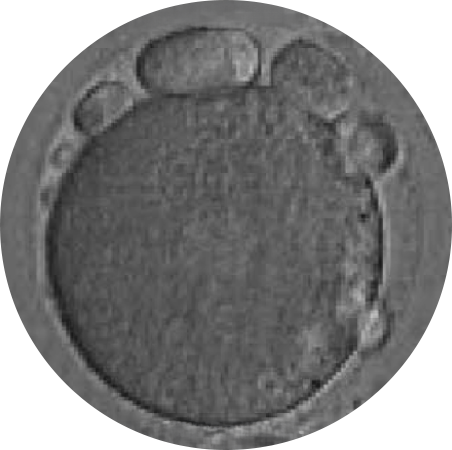
POOR OOCYTE QUALITY
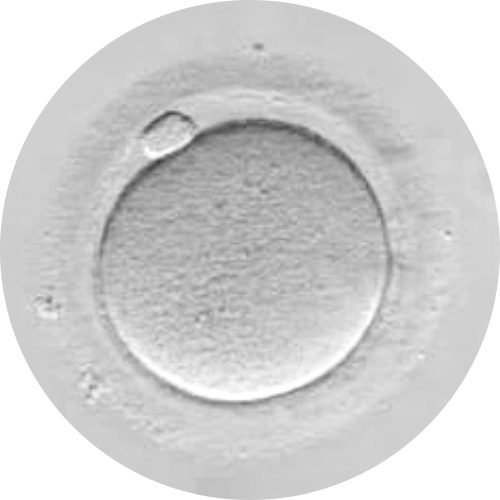
RESTORED EGG
1. Advanced Metabolic Diagnosis
Before proceeding with restoration, an evaluation of the metabolic state of the eggs is conducted. After egg retrieval, oocyte cytoplasm samples are extracted and analyzed for ATP, NADPH, and other key molecules. If an energy deficit is detected, restoration is performed using cytoplasm obtained from the patient’s own cells.
2. Infusion of Growth Factors & Metabolic Regulators
Growth factors derived from the patient’s own cytoplasm are injected, along with metabolic cofactors that enhance mitochondrial function. This process restores energy production and reduces oxidative stress.
3. Enhanced Fertilization & Embryo Culture
Once restored, the eggs are fertilized using the best sperm selected through PICSI and are then cultured under optimized conditions. Studies have shown that embryos generated from restored eggs have:
- A higher blastocyst formation rate (advanced-stage embryos).
- Lower incidence of chromosomal errors, reducing the need for egg donation.
4.Embryo Culture in Magnetic Fields
One of the most innovative breakthroughs of IVF MORE® is the use of magnetic fields to reorganize the internal structure of the oocyte.
Magnetic fields are applied after fertilization to create the energy needed for the oocyte’s cytoskeleton and the embryonic cells to divide properly. The cytoskeleton contains microfilaments that function like an internal “scaffold.” If these structures are disorganized, the oocyte cannot divide correctly, resulting in embryos with genetic abnormalities.
Applying a magnetic field during embryo culture allows for:
- Better distribution of mitochondria within the oocyte.
- Activation and deactivation of calcium and magnesium channels, which are essential for cell division.
- Reduced energy expenditure on cytoskeletal reorganization, allowing the oocyte to focus its energy on proper development.
If the metabolic diagnosis shows that the oocytes have low quality and cannot be restored using the patient’s own cells, metabolic factors from a donor oocyte may be transferred to recover the patient’s oocytes—while preserving the patient’s original genetic material entirely. Remember: without good metabolic material, the embryo division will not occur properly.
Magnetic Fields – Nature: https://www.nature.com/articles/srep37407
How an Egg Becomes a Viable Embryo
To generate a viable embryo, an egg must function efficiently in metabolism and cellular structure. However, due to aging or medical conditions, eggs may lose their division capacity and developmental potential, reducing the chances of a successful pregnancy.
1. Key Requirements for a Viable Egg
✔ Sufficient Cellular Energy
- Eggs require adequate ATP production for correct post-fertilization division.
- With age, ATP generation declines, increasing the risk of genetic errors.
✔ Cytoskeletal Integrity
- The egg’s internal microfibers support its structure and division process.
- If disorganized, chromosomal misalignment occurs, leading to genetic abnormalities.
✔ Correct Genetic Signaling & Metabolic Pathways
- Eggs activate specific genes regulating development and embryo formation.
- Metabolic pathways impact energy efficiency:
- Aerobic (optimal) → Efficient energy production.
Anaerobic (inefficient) → Leads production of toxic products.
- Low-quality eggs tend to rely on anaerobic metabolism, reducing embryo viability.
Desregulación metabólica en los ovocitos de pacientes con baja reserva ovárica: Zhu, Q., Li, Y., Ma, J., Ma, H., & Liang, X. (2023). Potential factors result in diminished ovarian reserve: a comprehensive review. Journal of Ovarian Research, 16(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13048-023-01296-x
2. Differences Between Restored & Non-Restored Eggs
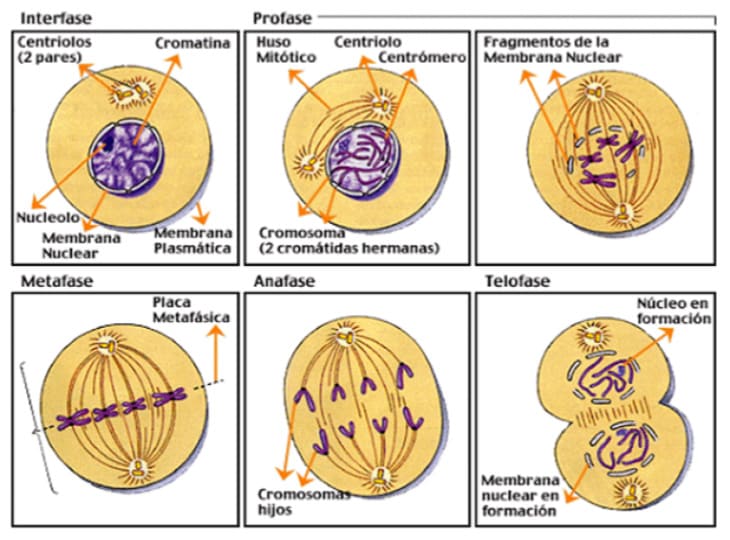
The eggs provide the acrosomal spindle responsible for dividing the genetic material after fertilization.
Genetic errors that occur during this step are the most important reason why an embryo fails to implant and are the leading cause of early miscarriage.
In women with low-quality eggs (due to advanced age, endometriosis, PCOS, etc.), the cytoskeleton may be disorganized or weakened, which affects the formation of the acrosomal spindle.

If the spindle does not form properly:
- The egg cannot correctly divide its genetic material.
- This can lead to embryos with chromosomal errors, such as trisomies (e.g., Down syndrome).
With IVF MORE®:
- The egg’s metabolism is restored and the cytoskeleton is reorganized.
- This improves the formation of the acrosomal spindle, supporting accurate genetic division.
- The result is a higher number of viable embryos and a lower rate of genetic abnormalities.
Characteristics
Non-Restored Eggs
🟢 Restored Eggs with IVF MORE®
Studies show that in women with poor egg quality, IVF MORE® can triple viable embryo rates and reduce chromosomal abnormalities from 82% to 26%, providing a groundbreaking alternative for those seeking pregnancy with their own eggs.
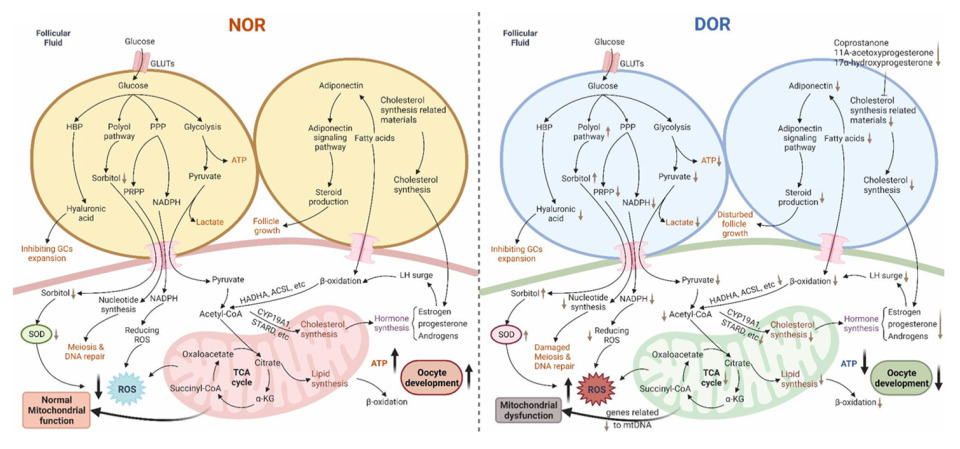
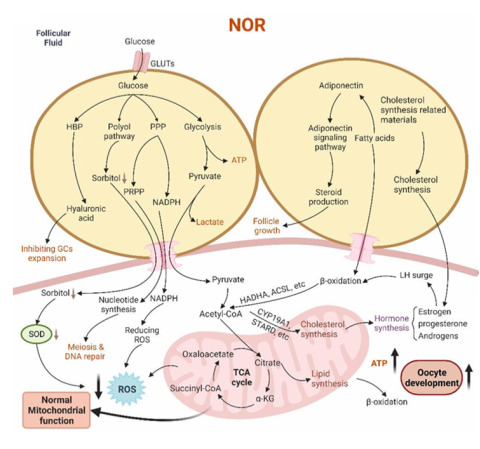
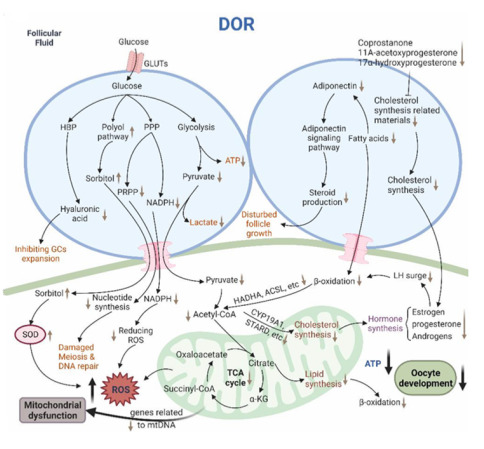
Zhu, Q., Li, Y., Ma, J., Ma, H., & Liang, X. (2023). Potential factors result in diminished ovarian reserve: a comprehensive review. Journal of Ovarian Research, 16(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/
Demographic Trends
1. Delayed Motherhood
Did you know that, over the past few decades, women have been postponing motherhood? This has happened for various reasons:
✔ Prioritizing career development and financial stability.
✔ Increased access to contraceptive methods.
✔ Changes in family and relationship dynamics.
✔ Rising average age for first-time mothers in many countries.
However, delaying pregnancy has a direct impact on fertility, as egg quality progressively declines with age.
2. Impact on Egg Quality
Did you know both ovarian quality (the number of available eggs) and egg quality begin to decline significantly after age 35? This decline is caused by several factors:
✔ Natural Egg Loss:
Women are born with approximately 1-2 million eggs.
By age 30, only about 100,000 eggs remain.
By age 40, only about 10,000 eggs are left, many of which exhibit metabolic impairments.
✔ Metabolic and Genetic Deterioration:
As women age, eggs accumulate DNA damage, increasing the risk of chromosomal abnormalities (such as Down syndrome).
Aged egg mitochondria produce less energy, affecting their ability to develop properly.
✔ Rising Infertility Rates:
1 in 6 couples face fertility challenges.
More than 50% of female infertility cases are directly linked to age-related ovarian decline.
Without medical intervention, the natural pregnancy rate after age 40 is below 5% per cycle.
3. IVF MORE®: A Response to the New Reproductive Reality
Thanks to advances like IVF MORE®, it is now possible to restore eggs that were previously considered unviable, offering new opportunities for women seeking to become mothers at an older age.
By optimizing egg quality through:
✔ Restoration of energy metabolism.
✔ Organization of the cellular cytoskeleton.
✔ Reduction of genetic alterations.
IVF MORE® is positioned as the most advanced alternative in assisted reproduction, allowing more women to achieve pregnancy with their own eggs, even after age 40.IVF MORE® se posiciona como la alternativa más avanzada en reproducción asistida, permitiendo que más mujeres logren su embarazo con sus propios óvulos, incluso después de los 40 años.

INDICATIONS
Who Can Benefit from IVF MORE®?
✔ Women over 35 with low ovarian reserve.
✔ Patients with severe endometriosis affecting egg quality.
✔ Women with PCOS who have experienced embryo development failure.
✔ Patients with previous failed IVF cycles due to poor egg quality.
✔ Women with previously vitrified eggs who want to enhance their potential before fertilization.
IVF MORE® is ideal for:
We suggest you read the following articles that explain how the eggs are affected by these pathologies:
- Desregulación metabólica en los ovocitos de pacientes con baja reserva ovárica: Zhu, Q., Li, Y., Ma, J., Ma, H., & Liang, X. (2023). Potential factors result in diminished ovarian reserve: a comprehensive review. Journal of Ovarian Research, 16(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13048-023-01296-x
- Ovario poliquístico: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17148555/ + https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34552933/
- Endometriosis: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC10342681/pdf/jcm-12-04186.pdf + https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23834505/ + https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5173290/pdf/nihms801246.pdf + https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31211846/
- Edad avanzada, el óvulo comete errores genéticos: Large cytoplasm predisposes oocytes to meiotic errors: http://www.cdb.riken.jp/en/news/2017/researches/0629_10912.html#:~:text=The%20oocyte%27s%20large%20cytoplasm%20is,segregation%20errors%20observed%20during%20meiosis
Studies conducted on IVF MORE® have shown promising results:
✔ Higher viable embryo rates – In women with poor egg quality, viable embryos increased up to 3x, with 70% of restored embryos developing successfully.
✔ Lower genetic risks – Chromosomal abnormalities decreased from 82% to 26%, similar to young donor eggs.
✔ Higher implantation & pregnancy rates – Women over 40 who previously had no viable embryos can now conceive using their own eggs.
Currently, an article is uner development which will explain these findings.


While IVF MORE® is a groundbreaking technique for egg restoration, it has certain limitations.
Who is NOT a Candidate for IVF MORE®?
The main limitation is a total absence of eggs. This technique improves egg quality but cannot create new eggs: without a mature egg to restore, the treatment cannot be done.
In some cases, there are patients who have stopped menstruating but can still produce at least one egg with ovarian stimulation. If a patient is still able to generate an egg, IVF MORE® is a viable option to improve her chances of achieving pregnancy with her own genetic material.
If no viable eggs are present, egg donation may be considered as an alternative to help her become a mother.
Edad avanza, el óvulo comete errores genéticos: Large cytoplasm predisposes oocytes to meiotic errors: http://www.cdb.riken.jp/en/news/2017/researches/0629_10912.html#:~:text=The%20oocyte%27s%20large%20cytoplasm%20is,segregation%20errors%20observed%20during%20meiosis
Alternatives:
Ovagen
For patients with extremely low ovarian function, we offer Ovagen, a treatment designed to reactivate ovarian function using growth factors and cellular regeneration.
If you’re unsure about your eligibility for IVF MORE®, our medical team can evaluate your case and recommend the best option.
Egg Donation
If the patient does not have any viable eggs, egg donation may be considered as an alternative to help her become a mother.
Discover How IVF MORE® Can Help You Achieve Pregnancy
Learn more about the technique that restores your eggs.
