What is IVF MORE®?
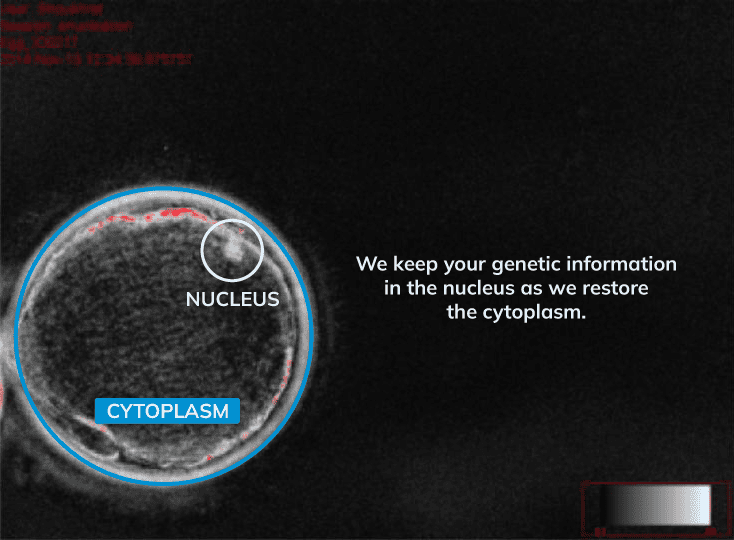
Cytoplasm restoration to improve egg metabolism while preserving your genetic material.
IVF MORE® (Magnetic Ovulatory Restoration) is an advanced fertility treatment that allows the restoration of poor-quality eggs, especially in women with advanced age, endometriosis, polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), or repeated IVF failures.
Unlike egg donation, IVF MORE® uses your own eggs, optimizing their ability to divide and fertilize without altering your genetic material. It represents a new patented scientific paradigm that restores and improves egg quality, giving you the opportunity to build a family with your own genetic resources.
Why does egg quality decrease?
As we age or in the presence of certain conditions, eggs show:
- Energy deficiencies (less ATP) preventing proper cell division.
- Oxidative stress that damages DNA and mitochondria.
- Disorganization of the cytoskeleton, key for genetic division.
- Genetic errors that result in abnormal embryos or implantation failures.
These factors increase the risk of early miscarriage and make it more difficult to achieve pregnancy.
IVF MORE® and the Demographic Reality: A Scientific Response to a Global Change
Postponing Motherhood: A Shift in Society
Over the past decades, women’s reproductive profiles have radically changed. Today, more and more women are choosing to postpone motherhood due to multiple social, professional, and personal factors such as:

The Biological Challenge: Egg Quality and Age
As age advances, egg quality is also affected due to profound changes in metabolism and structure. These factors combine to decrease the chances of pregnancy, increase reproductive risks, and elevate failure rates in traditional fertility treatments.
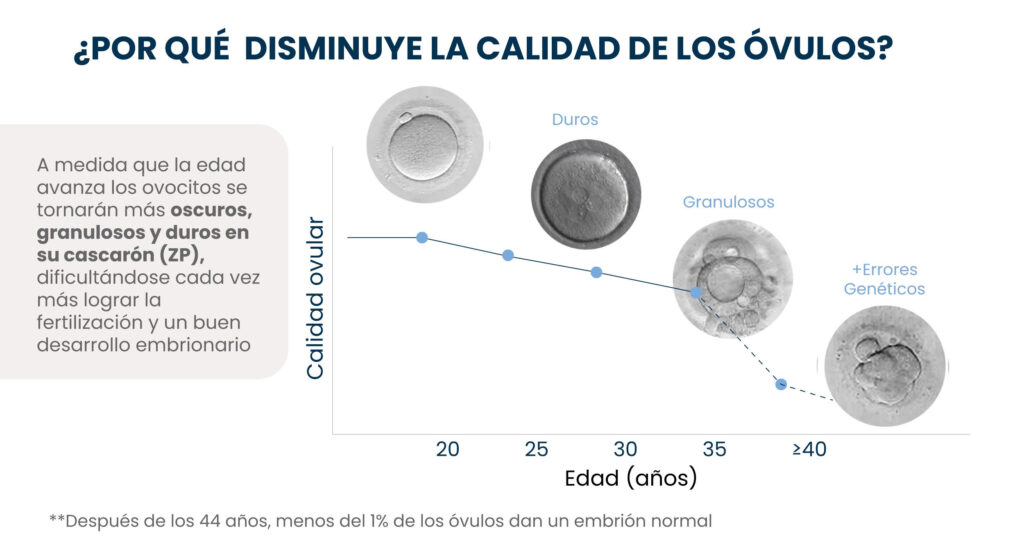
Some of the main problems include:
Progressive loss of available eggs.
While women are born with up to 2 million eggs, this reserve drastically decreases over time. By age 30, only 5% remains, and by age 40, only 1%, many of which present metabolic and structural abnormalities affecting their reproductive capacity: they no longer have the energy or structure needed to create life.
Mitochondrial deficiencies:
Low cellular energy (ATP) essential for proper embryo division.
Increased oxidative stress
and accumulated damage to egg DNA.
Genetic errors in meiosis,
promoting the appearance of aneuploidies like Down syndrome.
Disorganization of the cytoskeleton
affecting the proper chromosomal distribution.
Esto tiene un alto costo en fertilidad: Hoy, 1 de cada 6 parejas enfrenta dificultades para concebir. En mujeres, más del 50% de los casos de infertilidad están directamente ligados al envejecimiento ovárico. A los 40 años, más del 75% de los óvulos pueden presentar alteraciones cromosómicas, y la posibilidad de embarazo natural por ciclo cae por debajo del 5%. Sin intervención médica, el tiempo se convierte en el mayor enemigo de la fertilidad.
The Global Problem:
Infertility and the Demographic Crisis
Postponing motherhood does not only affect individuals. Demographic consequences are already visible in many regions of the world, with birth rates below the population replacement level:
According to the WHO, 1 in 6 people worldwide face fertility problems.

In countries like Italy, South Korea, or Japan, birth rates are among the lowest on the planet, threatening the sustainability of economic and social systems.
In Latin America, fertility rates have dropped by more than 50% since 1960.
This scenario requires the development of innovative medical solutions, like IVF MORE®, to preserve and restore fertility in women who cannot conceive at younger ages.
The Solution: IVF MORE®
for the New Reproductive Reality
IVF MORE® arises as a direct response to this challenge. It is not just another fertility treatment: it is an advanced egg restoration technique without altering the genetic load that allows for the improvement of egg quality while preserving genetic integrity. Unlike egg donation, IVF MORE® aims to preserve the patient’s genetic identity, even when their eggs have a low metabolic or structural capacity.
Thanks to this technology in development:
Women of advanced age can have access to restored eggs with greater potential for fertilization, embryo development, and pregnancy.
The need for egg donation is reduced, especially in cases where viable eggs are still available.
The effects of ovarian aging, one of the main barriers in contemporary female fertility, are mitigated.
A New Paradigm: Reproductive Science with Purpose
IVF MORE® represents not only an advancement in regenerative medicine but also a tool that concretely responds to the demographic and social changes of the modern world. With the scientific backing of leading researchers like Dr. Shoukhrat Mitalipov, this technique aims to restore the potential of eggs and offer more women the opportunity to become mothers with their own genetic material, even at life stages when this seemed impossible.
Motherhood at advanced ages is no longer a promise for the future. With IVF MORE®, it is a real possibility, based on science
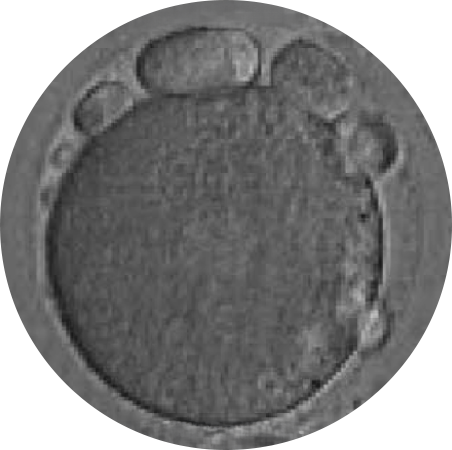
POOR EGG QUALITY
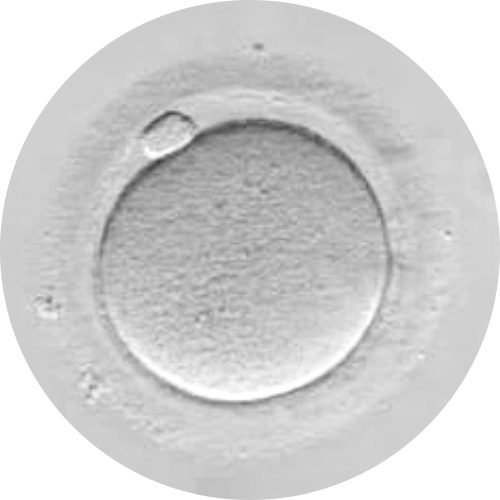
RESTORED EGG
What does an egg need to generate a viable embryo?
Over time or due to medical conditions, eggs lose their ability to develop. To form a healthy embryo, the egg must meet:
- Sufficient cellular energy:
It must produce high levels of ATP to divide and develop properly.
As age advances, this ability drastically decreases.
literatura: Desregulación metabólica en los ovocitos de pacientes con baja reserva ovárica: Zhu, Q., Li, Y., Ma, J., Ma, H., & Liang, X. (2023). Potential factors result in diminished ovarian reserve: a comprehensive review. Journal of Ovarian Research, 16(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13048-023-01296-x
- Cytoskeleton integrity:
The internal microfibrils organize the chromosomes during division.
If damaged, division is defective and leads to genetically erroneous embryos.

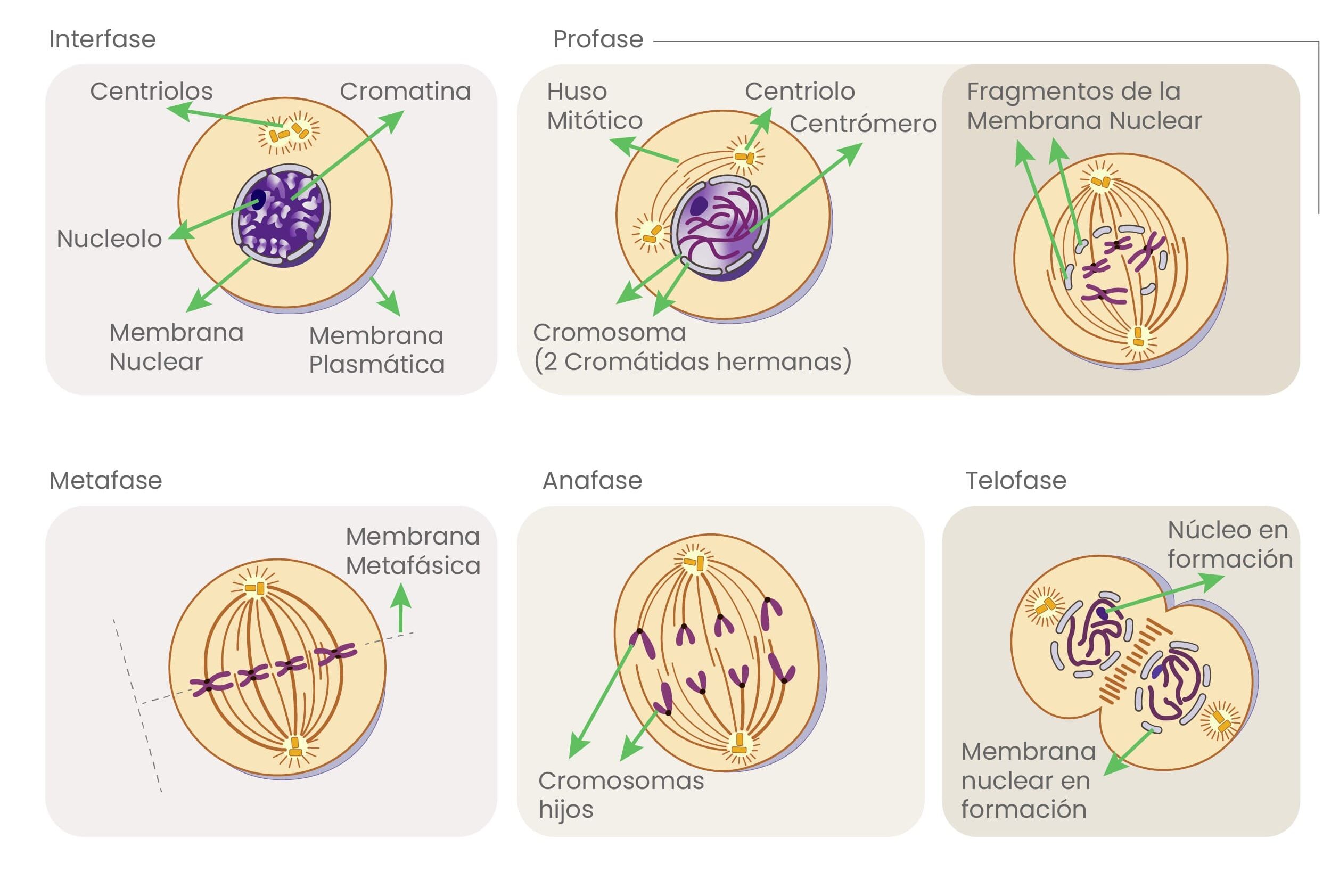
- Correct genetic signaling and metabolic pathways:
Eggs must activate specific genes to direct their development.
In aged eggs, anaerobic pathways dominate, generating inefficient energy and accumulating toxic waste.
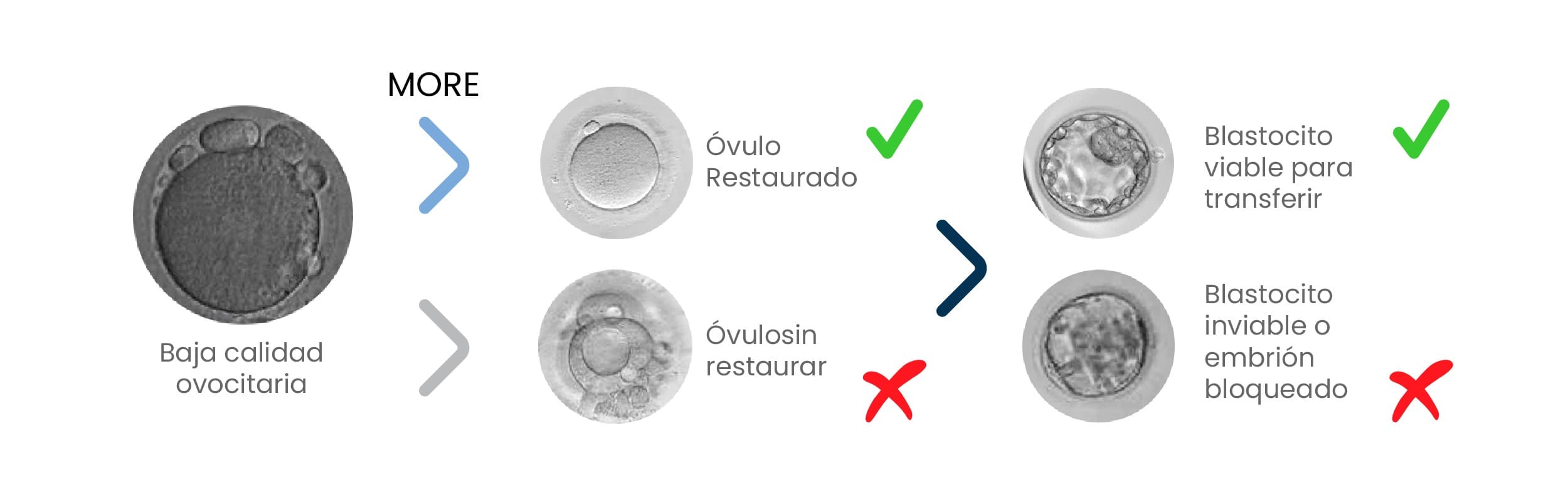
How does IVF MORE® work?
The treatment is performed in highly controlled phases in a laboratory that integrates multiple scientific advances:
* Ovarian Metabolic Diagnosis
Eggs are collected to evaluate their energy competence and mitochondrial functionality.
Mitochondria (the “energy factories” of the cell) provide the molecules ATP, NADPH, and other key molecules indicating the egg’s ability to generate energy.
If an energy deficit is detected, metabolic restoration is carried out.
* Cytoplasmic Restoration: IVF MORE®
Metabolic and mitochondrial factors are infused. This step involves highly specialized equipment designed for this technique that allows for advanced and highly controlled micromanipulation techniques to achieve the best results.
- This optimizes mitochondrial function, improves energy production, and reduces oxidative stress, two key pillars for a healthy and functional egg
If the egg’s cytoplasm is not suitable, it may require cytoplasm from a compatible donor egg, without altering the patient’s DNA.
In severe cases, if it is not possible to restore the metabolism using the patient’s own cells, metabolic material from a donor egg can be transferred without modifying the nuclear DNA, preserving 100% of the patient’s genetic material.
* Fertilization and Optimized Embryo Culture
After restoration, the eggs are fertilized with the best sperm (selected through techniques like PICSI or ICSI), and cultured under highly controlled conditions.Observed results:
- Higher blastocyst (embryo) formation rate.
- Lower incidence of chromosomal errors (aneuploidies).
- Significant reduction in the need for egg donation.
* Culture with Magnetic Fields
The cytoskeleton of the egg, which acts as its “internal structure”, must be organized to ensure proper cell division. In aged or poor-quality eggs, this structure is weakened or disorganized.
Magnetic fields help:
Reorganize the egg’s cytoskeleton.
Improve mitochondrial distribution within the cell.
Activate essential ionic channels like calcium and magnesium.
Reduce unnecessary energy expenditure, allowing the egg to focus on its development.
Literature: Magnetic Fields – Nature: https://www.nature.com/articles/srep37407
The IVF MORE® technique requires egg retrieval to be performed in Ingenes’ specialized laboratory in Mexico City.
This technique is under development, protected by a patent, and has scientific articles in the process of being published in peer-reviewed scientific journals.
Literature:
- Autologous Germline Mitochondria Energy Transfer : https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5545901/pdf/nihms880936.pdf
- Shoukhrat Mitalipov, Ph.D. / Center for Embryonic Cell and Gene Therapy : Meet Shoukhrat Mitalipov, Ph.D./ His pioneering work with mitochondria could help eliminate genetic disease: https://www.ohsu.edu/embryonic-cell-gene-therapy-center/meet-shoukhrat-mitalipov-phd
- Magnetic Fields – Nature: https://www.nature.com/articles/srep37407
How does IVF MORE® help prevent genetic errors?
- 1. Cytoskeleton: It is the egg’s “scaffold.” It organizes its components and guides cell division.
- 2. Acromosomal Spindle (Meiotic Spindle): It forms from the cytoskeleton and is responsible for aligning and correctly distributing chromosomes at fertilization.
What happens when an egg is of low quality?
In conditions like advanced age, endometriosis, or polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), the egg loses metabolic and energy efficiency. This results in:
- 🔻 Cytoskeleton disorganization
- ⚠️ Spindle instability
- ❌ Imbalanced cell division
The consequence?
Chromosomal distribution errors, leading to trisomies (e.g., Down syndrome), monosomies (e.g., Turner syndrome), or non-viable embryos or early miscarriages.
IVF MORE®:
Restoration for Precise Genetic Division
IVF MORE® works on the root cause: the egg’s cellular metabolism.
- By restoring the cytoplasm with energy factors, growth factors, and functional mitochondria from the patient:
- The acromosomal spindle is stabilized.
- The cytoskeleton is reorganized.
- The ability to divide chromosomes accurately is restored.
The result: A dramatic decrease in genetic errors, increasing embryo quality and providing a higher chance of pregnancy with your own eggs.
Characteristics
Non-Restored Eggs
🟢 Restored Eggs with IVF MORE®
Scientific Evidence
IVF MORE® can triple the rate of viable embryos and reduce genetic abnormalities from 82% to 26%, providing an effective alternative for those who wish to achieve pregnancy with their own eggs.
This technology was developed with Dr. Shoukhrat Mitalipov (Oregon), a world leader in mitochondrial biology.
More than 19 babies have been born using this technique, with scientific publications in progress.
Who is IVF MORE® for?
This treatment is recommended for:
- Women over 35 with poor egg quality.
Desregulación metabólica https://doi.org/10.1186/s13048-023-01296-x
- Patients with endometriosis.
- Women with PCOS and embryo blockage.
Ovario poliquístico: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17148555/ + https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34552933/
- Women who wish to use vitrified (frozen) eggs and improve their quality before fertilization.
Edad avanzada, el óvulo comete errores genéticos: Large cytoplasm predisposes oocytes to meiotic errors: http://www.cdb.riken.jp/en/news/2017/researches/0629_10912.html#:~:text=The%20oocyte%27s%20large%20cytoplasm%20is,segregation%20errors%20observed%20during%20meiosis
Ovocitos Anormales
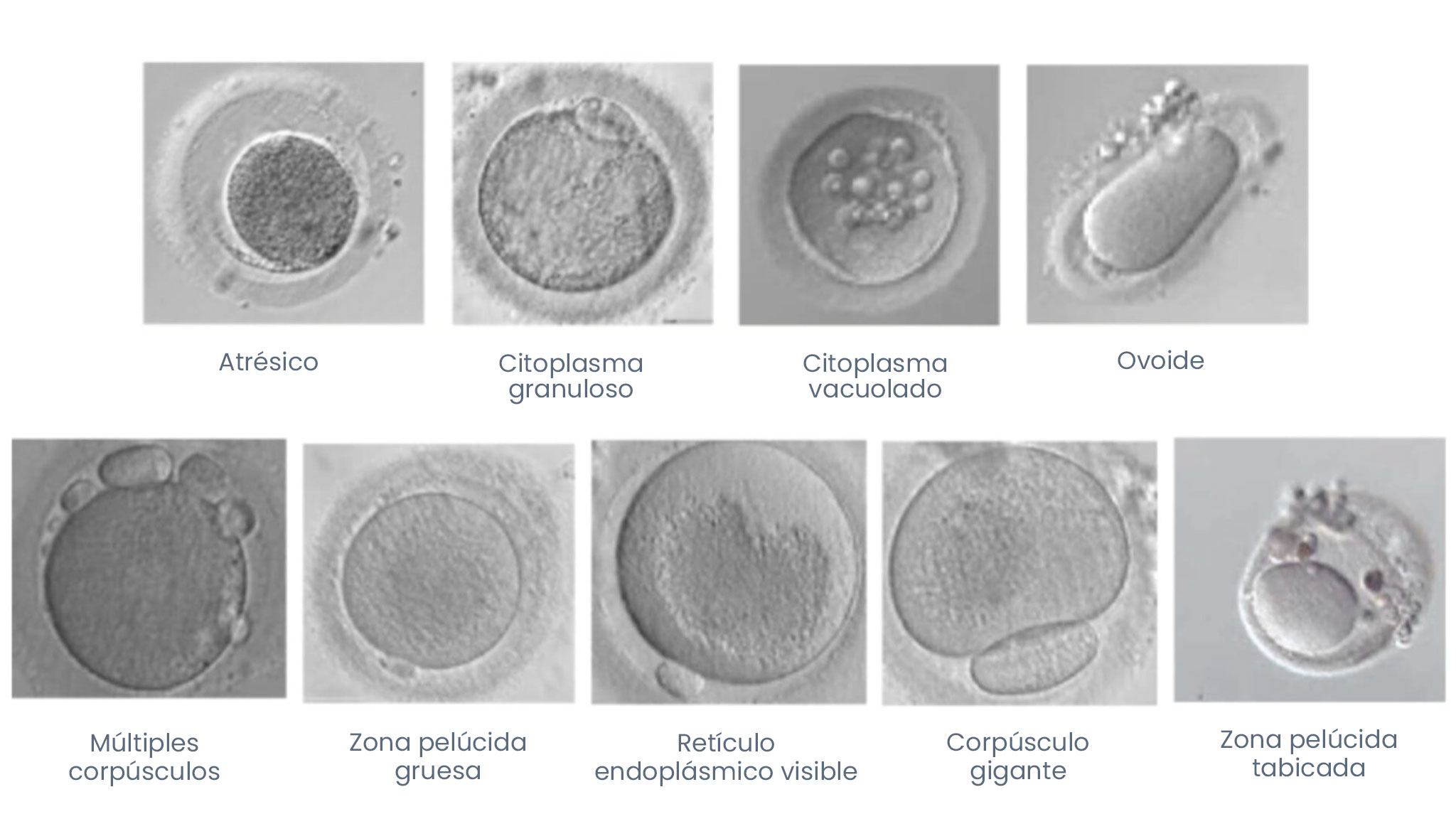
Studies with IVF MORE® have shown promising results for women of advanced age, with endometriosis, or polycystic ovary syndrome:
- Higher viable embryo rate: In women with poor egg quality, the number of viable embryos increased up to three times compared to non-restored eggs, with 70% of restored embryos being viable.
- Reduced genetic risk: The rate of embryos with chromosomal abnormalities decreased from 82% to 26%, a percentage similar to young donor eggs.
- Higher implantation and pregnancy rates: Patients over 40 who previously couldn’t achieve viable embryos are now able to get pregnant with their own eggs.
Currently, an article is in progress to support these findings.



IVF MORE® is a revolutionary technique that restores egg quality, but there are cases where its application is not possible.
Patients who are not candidates for IVF MORE®
The main limitation for IVF MORE® is the total absence of eggs. This technique is designed to improve egg quality: without a mature egg to restore, the treatment cannot be carried out.
In some cases, there are patients who have stopped menstruating but can still produce at least one egg with ovarian stimulation. If a patient can still generate an egg, IVF MORE® is a viable option to improve their chances of pregnancy with their genetic material.
If the patient has no viable eggs, egg donation may be the alternative for them to become mothers.
Are there alternatives?
Learn about Ovagen
For patients who face extremely low ovarian response or egg reserve, there is a complementary option: Ovagen.
This innovative treatment is designed to reactivate ovarian function in cases where egg production is minimal. Through a growth factor and cellular regeneration approach, Ovagen can help some patients recover ovarian function and retrieve eggs after stimulation, giving them a new opportunity to attempt pregnancy with their own genetic material.
If you have questions about your eligibility for IVF MORE®, our medical team can evaluate your case and recommend the best option for you.
Egg Donation
If the patient has no viable eggs, egg donation can be used as an alternative for achieving pregnancy.
Discover how IVF MORE can help you achieve your pregnancy
Learn more about the technique that restores your eggs.
